Building a CI/CD Pipeline with Jenkins and GitHub
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to CICD
- 2. Tools and Technologies
- 3. Setting Up CI/CD with Jenkins and GitHub
- 4. Testing Your Pipeline
- 5. Deploying Application
- 6. Rollback and Recovery
1. Introduction to CICD
1.1 What's CICD
- What CICD Can Do: Automate the entire software development process.
- What CI/CD pipeline automates: the building, testing, and deployment of software code, making the entire process faster, more efficient, and less error-prone.
- What we used to deploy before CI/CD:
- Compare the old way and the new way
1.1 How deployment looked in the old world without CICD
CICD’s benefits always be mentioned:
- Higher efficiency
- Reduced risk
- Faster product delivery.
But no one tell the details of why it is faster and lesser risk. The development process when I was an intern(Before having CICD) was like developers have to deploy the environment with the help of the operations team because have no permission to access production servers.
The delivery of the program to the operations team was done manually, including the packaging such using “tar czvf app.tar.gz “and tools such as “scp” to transfer the compressed file.
Once the operations team received the program package, they had to deploy based on manual processes or bash shell scripts, and they could not even be sure if the application had been tested enough…
If a bug occurs in the production environment, the time spent on the above complex steps is wasted. then rolled back manually and the above steps must be repeated, causing further delays and wasting more time. This what the error-prone and time-consuming of manual process refer
The inefficiencies of manual deployment processes is important to know for people especially who are new to the industry
☞ Demo of the deployment process using Bash Shell in ancient time
1.2 Necessary Plugins for Jenkins
If you want to set up a CI/CD pipeline using Jenkins, you will need to install some plugins to support the various stages of the pipeline. Here are some plugins that are commonly used in CI/CD pipelines:
- Git Plugin: This plugin allows Jenkins to interact with Git repositories, enabling you to check out code from a repository, push changes, and trigger builds based on Git events.
- Pipeline Plugin: This plugin enables you to define your CI/CD pipeline as a script, which can be stored in a Jenkinsfile in your code repository. It provides a powerful syntax for defining build stages, integrating with other plugins, and executing shell commands.
- Docker Pipeline Plugin: This plugin allows Jenkins to build, tag, and push Docker images as part of your CI/CD pipeline. It provides a syntax for defining Dockerfile instructions and integrating with Docker Compose.
- Credentials Plugin: This plugin enables Jenkins to securely store and manage credentials, such as usernames and passwords, SSH keys, and API tokens.
- Build Timeout Plugin: This plugin allows you to set a maximum time limit for each build stage, which can help prevent builds from hanging indefinitely and consuming resources.
- Slack Notification Plugin: This plugin enables Jenkins to send notifications to Slack channels or users, providing real-time feedback on build status, failures, and other events.
1.3 CI/CD Workflow Overview
pass
2. Tools and Technologies
There are several common ways to implement CICD, but one of the most popular methods is to use a combination of a version control system (such as Git), a continuous integration server (such as Jenkins), and a deployment tool (such as Ansible or Docker). So we just chose these as the tools to implement the CICD today :)
- GitHub
- Jenkins
- Docker
3. Setting Up CI/CD with Jenkins and GitHub
3.1 Setting Up a Jenkins Project
- Setting up the credentials
- Generate a Secret string, there a few metod to generate it, i chose uuid
Dashboard > Manage Jenkins > Credentials > System > Global credentials (unrestricted)
- Setting up pipeline

1. xx 2. xx 3. xx
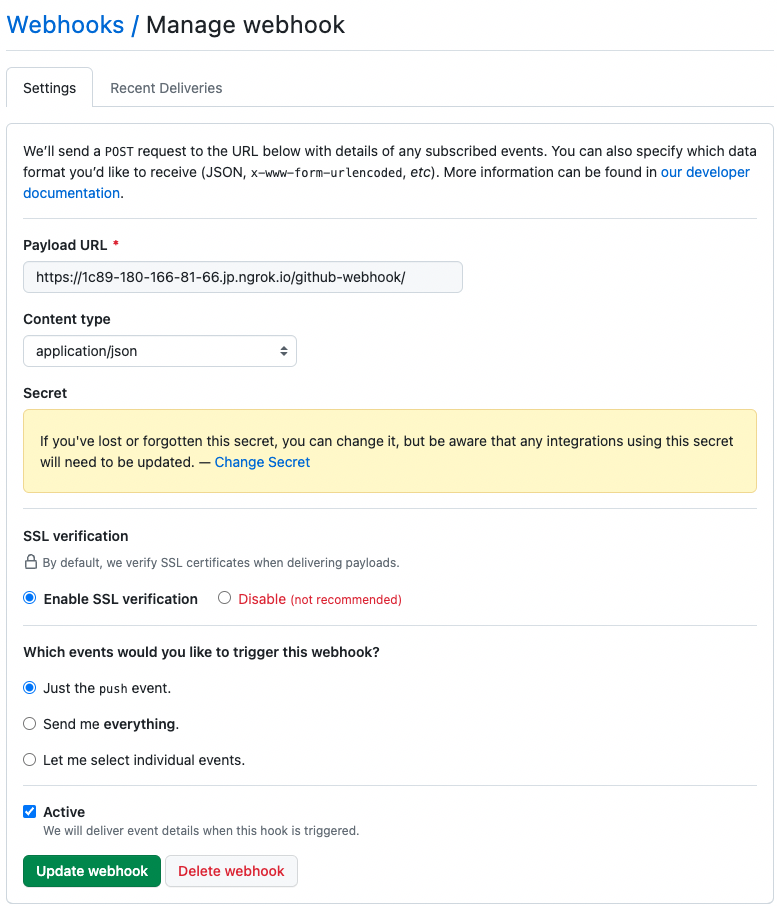
3.2 Setting Up Github
<div class="side-by-side clearfix">
<img class="left-image" src="assets/images/posts/build-a-blog/contents/cicd_github_img0.png" alt="Alt Text">
<figcaption class="caption">GitHub Webhooks Setting</figcaption>
<p class="right-text">
<span> Select your project => Settings => Webhooks </span>
</p>
</div>3.3 Connecting Jenkins to GitHub
pass
===
